developed to provide a common language for
requesting and supplying material within the
Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and the
General Services Administration (GSA). NAV-
SUP P-437, NAVSUP P-409, NAVSUP P485,
NAVSUPINST 4235.3 and the GSA Catalog,
which were previously explained, establish
guidelines and procedures for using the
MILSTRIP System.
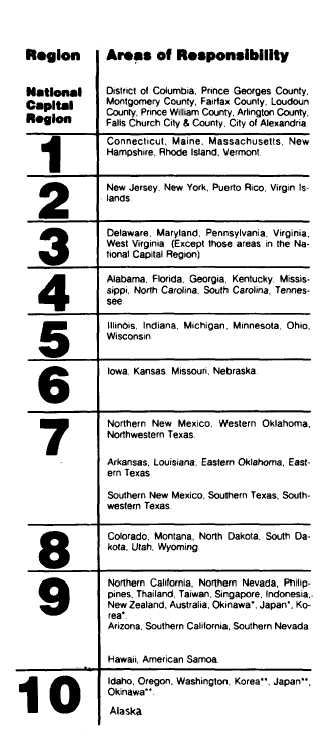
Figure II-2-7.—Areas of Responsibility of the Regional
Offices of the General Services Administration (GSA).
A vital and integral part of the MIL-
STRIP System is the Uniform Material Move-
ment and Issue Priority System (UMMIPS). The
illustration in figure II-2-9 shows that
MILSTRIP and UMMIPS are used worldwide
by all the Armed Forces of the United States.
UMMIPS was established to ensure that
material requests are processed in accordance
with the military importance of the requesting
activity and the urgency of that activity’s needs.
This system provides the method of assigning
priorities for the issuing and movement of
material. Most of the items that need to be
acquired for use in the CRP are obtained on a
routine basis. Therefore, the chaplain and RP
need to plan program requirements well in
advance to ensure that ecclesiastical supplies are
available when needed.
The storekeeper in the supply department is
extensively involved with the preparation and
processing of MILSTRIP documents. A
Religious Program Specialist need not become
an expert in using this system. However, it is
important for the RP to know how to properly
prepare a requisition form. As figure II-2-10
illustrates, the RP should study and learn how to
use MILSTRIP procedures and codes as they
pertain to fulfilling the requirements of the
Command Religious Program.
MILSTRIP requisitioning is based upon the
use of a coded, single line item document for
each supply transaction. The documents listed
below are some of the forms that are used for
MILSTRIP requisitioning.
. DD Form
Single Line Item
(Manual).
2-11
1348—Department of Defense
Requisition System Document